Concorde Crash Disaster | One Crash That Killed Concorde | 113 People Dead In Concorde Air Crash
by user · September 15, 2022
INTRODUCTION
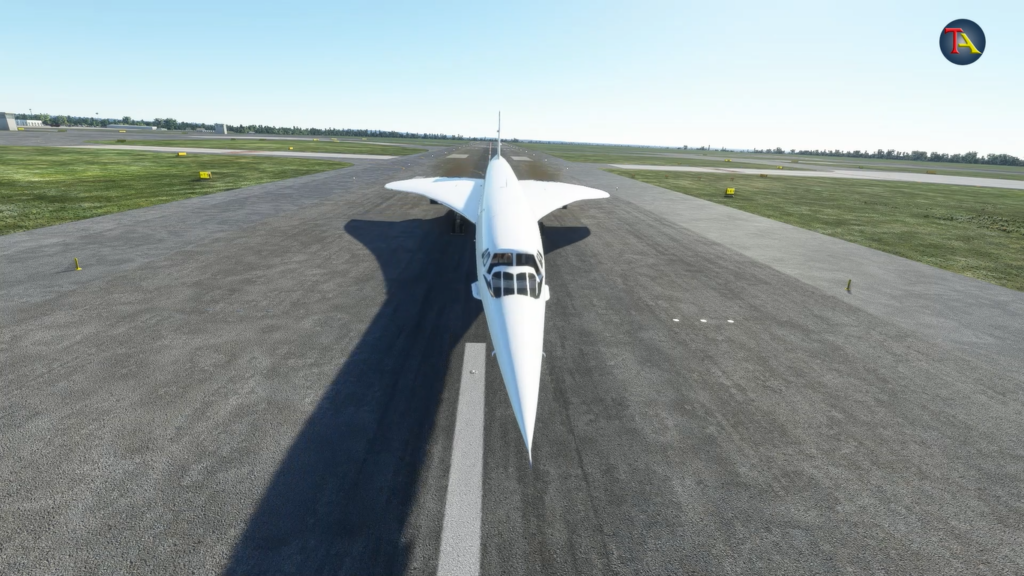

Concorde – World’s first supersonic airplane
The Concorde, the plane that flew faster than the speed of sound, was known as the triumph of modern engineering in the 20th century. In a tragic accident, its tires exploded, and the plane crashed. Since then, no one dared to board this flight. Let us see what exactly happened.
Case Study
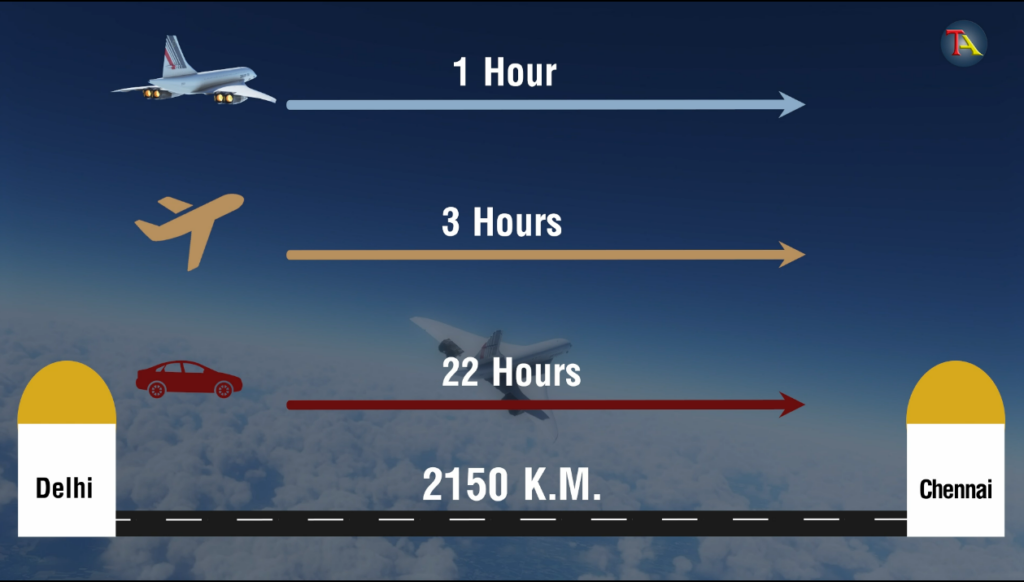
The distance between Delhi and Chennai is approximately 2150 km. Without breaks, it would take 22 hours to reach Chennai by car at 100 km/hr.
In an aeroplane, this distance is travelled in 3 hours.
However, Concorde was unique. It could cover this long distance in less than an hour!
Just imagine how the passengers would feel travelling in an aeroplane that runs at 2200 km/hr, faster than the speed of sound. It is hard for us to imagine how it would feel. But Concorde made that possible. About 25 years ago, Concorde made headlines across the globe. Its supersonic speed travelled people over 1000 kilometres in the blink of an eye.
However, unexpectedly, on 25th July 2000, a tragic incident shook the world. After that, no one dared to board the Concorde flight. That day, not only hundreds of innocent lives were taken, but also the plane Concorde vanished into thin air.

Before getting into the nitty-gritty of the accident, let us discuss some important points about the functioning of planes. This will help us understand the incident better.
As we previously discussed, Concorde was a supersonic aeroplane that flew two times faster than the speed of sound. To fly at such a high speed, the Concorde was designed with an exceptional body and wings having aerodynamic shapes. Indeed, you must have seen the majestic Delta wings design, a plane that looks like an eagle when it flies.
Due to its Delta wing design, Concorde could easily fly from subsonic to supersonic speed. But the Delta wing design came with its own difficulties. Concorde had to land at high speed and take off at a higher angle than standard planes. This allowed the plane to be lifted from the ground and remain in the air.
To understand this better, let us consider an example of a Boeing 737. This plane needs to run on the runway at a speed of 140 to 150 knots to takeoff, while a concorde plane needs 200 knots before taking off to be lifted easily in the air.

However, leaving the runway at such high speeds meant putting a lot of pressure on the tyres. For this reason, in the 30 years of its service, about 57 times the tires of Concorde would explode at the time of take off. Because the tires exploded at such high speeds, the debris of the tires would sometimes damage the lower ends of the wings. With time, this caused leakage in the fuel tank and damaged the hydraulics system of the Concorde. After inspection of such incidents, many changes were made to the tires of the Concorde and its hydraulics systems were suggested by experts.
Even though the investigation team knew the fuel leakage could cause the plane to catch fire, they did not take it seriously.
Concorde had four twin spool turbojet engines by Olympus. These were placed behind the delta wings just above the hydraulic system. The unique design and multiple air intake features enabled the Concorde to fly at supersonic speed.
With this, let us now discuss our case study and know more about what actually happened.
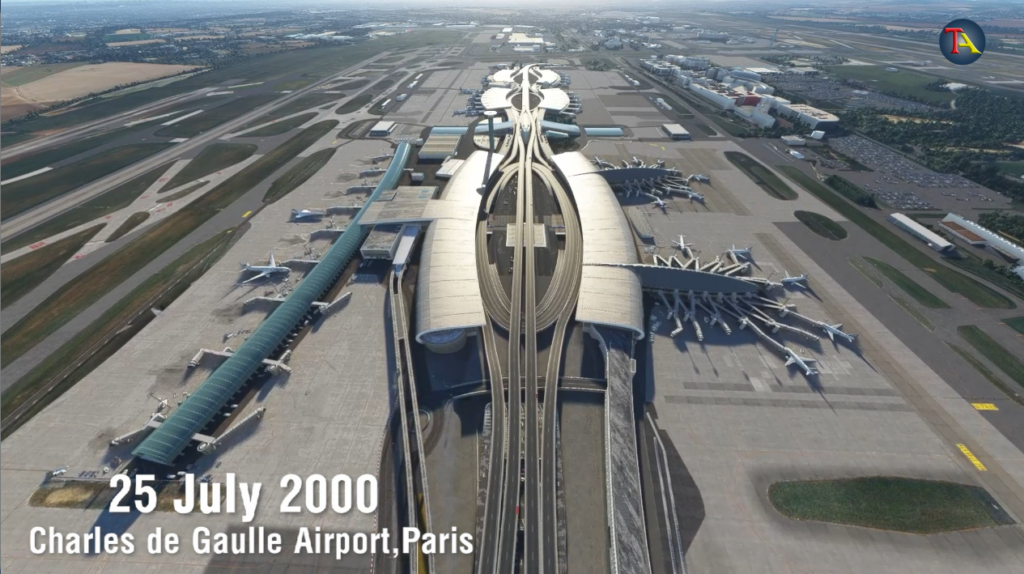

On 25th July 2000, Concorde’s Air France flight 4590 from Paris to New York was all set to fly. That day, from the beginning, the flight was facing technical errors, and because of this, they decided to switch the flights to another Concorde plane. After much debate, it was finally decided to go ahead with the same Concorde plane.
This was a chartered flight hired by a tourist company named ‘Peter Deilmann Cruises’. Most of the people on board were German tourists travelling to New York on a tour of 16 days.
That day, Captain Christian Marty, aged 53, was piloting the flight. In his 33 years of an aviation career, he has over 13,477 flight hours of experience. Of these, about 317 hours were spent flying the Concorde plane.
Other officials were also present, including First officer Jean Marcot and Flight engineer Gilles Jardinaud, aged 50 and 58. The flight crew was accomplished and specially trained to fly the Concorde plane.
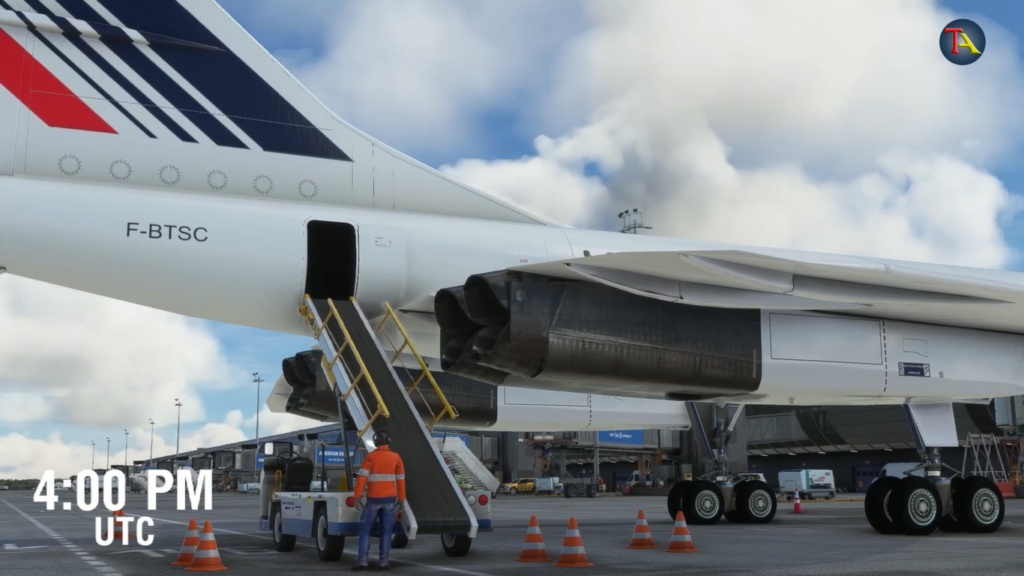

The cabin crew began the pre-checks of the flight around 4 pm.
After the ground engineer confirmed, the flight fuel tank was filled to almost its maximum fuel capacity of 95 tons.
At 4:25 pm, the flight started its push-back process and roared its engines sequentially.
Runway 26R was allotted to Concorde flight for take-off, the most enormous runway at Paris Airport.
By 4:35 pm, the Concorde flight started moving towards runway 26R.
When the Concorde flight was proceeding towards runway 26R, another flight, DC10, was taking off from the same runway. While taking off, a small metal part of the DC10 flight’s right engine separated and dropped on the runway. The flight’s crew was unaware of this mishap, so they took off as usual.
Without anyone’s knowledge, the metal part was lying on the runway on which the Concorde flight was going to take off.
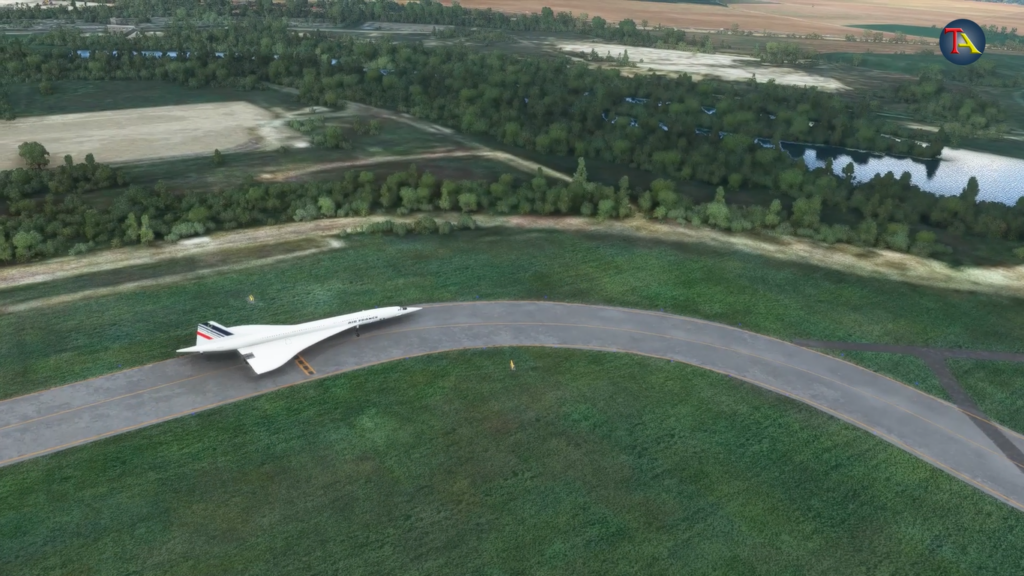

Proceeding slowly towards the runway, the flight was ready to take off. The flight crew then started the final briefing process. Usually, during these take-off briefings, the flight crew discusses all kinds of emergency situations that may occur during take-off that may lead to the cancellation of the flight.
Keeping in mind the speed of the plane, they decide that if there’s any issue in the plane running between 0-100 knots, then they shall cancel the take-off. If a problem arises between 100-150 knots, take-off will be cancelled only if the engines have not caught fire or the tyres haven’t burst. Finally, if the runway speed crosses 150 knots and an issue arises, the take-off will not be cancelled since it will be impossible to stop the aeroplane at that speed, and the plane might crash. Hence, it is considered wiser to re-evaluate and control the situation once the plane has taken off.
And finally, at approximately 4:42 pm, the Concorde flight began taking off.
To pick up take-off speed, the Captain thrusts forward all four levers with full force to lift the plane into the air.

Within minutes, the Concorde achieves a speed of 150 knots. At this speed, the plane cannot be stopped under any circumstances.
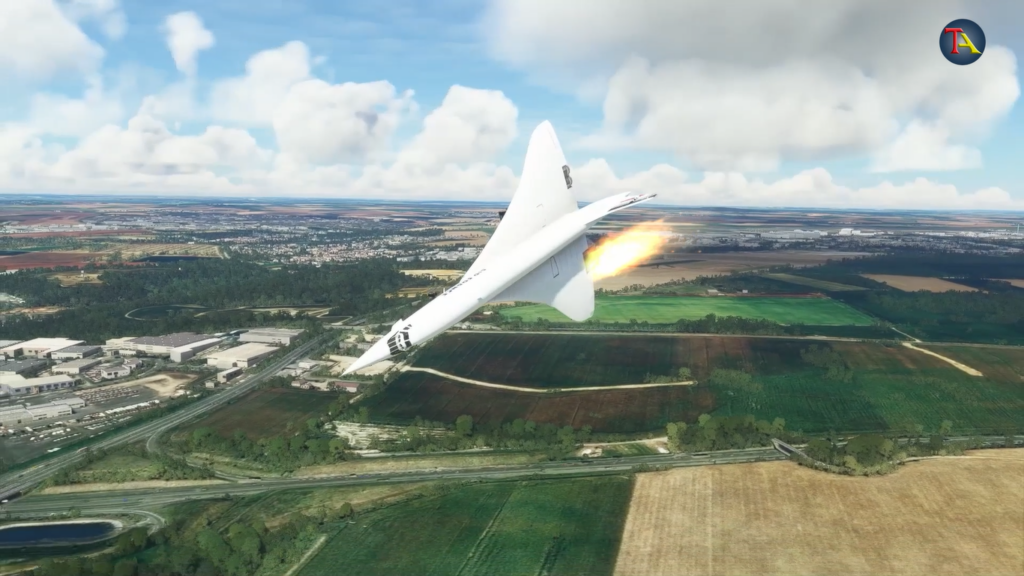
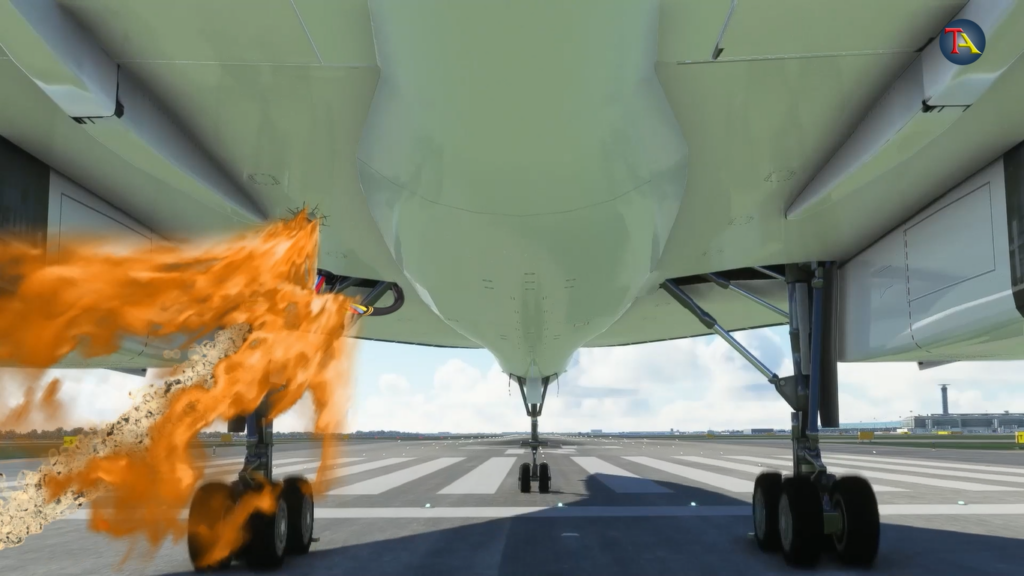
Suddenly, the plane’s left tire passed through the fallen metal part of DC10 and with a loud sound, the tires exploded.
Since the tires exploded at a very high speed, their parts scattered at a similar rate and started damaging the lower end of the plane.
The parts not only had great speed but abundant force, too. This caused a hole in the fuel tank at the bottom of the left wing. Since the tank was full, the fuel started leaking quickly.
Because of the collision between the tire debris and metal parts, the loading gear also gets damaged. Some wires also break, and due to the high speed, there is friction between the wires. When the leaking fuel comes in contact with these charged wires, it catches fire.
Because the tires burst on the runway, Concorde turned to the left, and the captain adjusted the radar pedal to control the plane’s direction.

As the fire rapidly spreads, it comes in contact with the two engines on the plane’s left side, thereby damaging them. Soon, both the left engines of the plane malfunctioned. The cockpit now receives warning signals of engine failure.
Pilots were just decoding the engine failure message, that their worst nightmares came to life. They received a message about the engines on fire.
The incidents took place in the blink of an eye. The plane had already caught fire even before the pilots and engineers could interpret and take action.
By now, the folks at the control tower were witnessing the Concorde on fire, and they tried to connect to the pilots on board to inform them of the fire.
However, it was too late to stop. Concorde was already at the speed of over 150 knots, and hence, it was impossible to stop the plane. The runway had almost ended, and the plane could crash with the airport boundary any minute. To avoid crashing, the pilot decided to take off. The plane had finally taken off, breaking some airport runway lights.
But, due to failed left engines and the rapidly spreading fire, the plane was tilting towards the left. The cockpit was still receiving flashes of fire warnings. Immediately, the flight engineer started the fire control procedure and lowered the engine thrusts. In addition, he activated the fire levers.
The Concorde was now flying at the speed of 750 m/sec and a height of 100 feet.
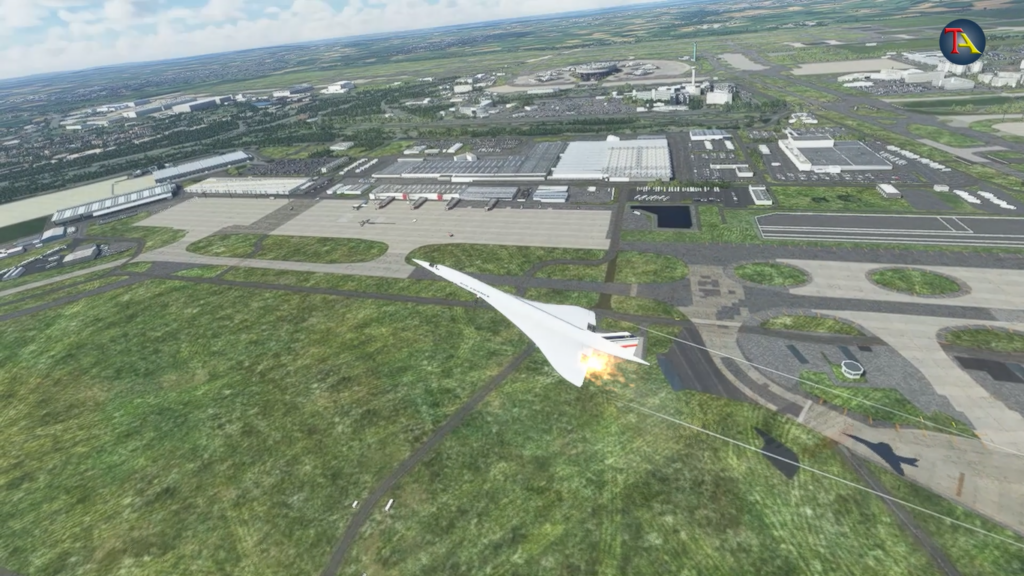

On the one hand, the plane was losing its speed due to failed engines, while on the other, the left wing and other control units were damaged due to fire. The pilots were trying their best to control the plane. The plane was now tilted by 113 degrees on the left side.
The pilot was trying his best to straighten up the plane. However, it was too late.
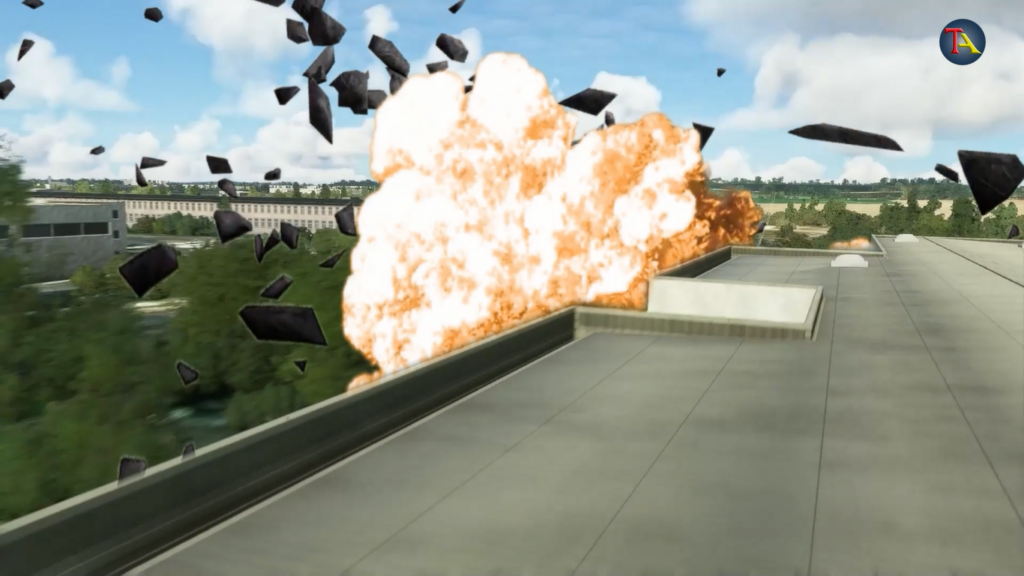
At about 4.44 pm, the Concorde crashed into a hotel in the Gonesse area. Since the fuel tank was full, the whole aeroplane caught fire after crashing.
Unfortunately, none of the passengers or crew members survived the crash. Due to this untoward incident, along with the 109 onboard passengers, 4 hotel staff died.
This was unimaginably an unfortunate incident for which an investigation was immediately scheduled.

After the investigation, the team concluded that the primary reason behind the crash was the explosion of its tyres. After which, the fuel tank caught fire, and both engines failed.
After this report, the Concorde plane lost its licence to fly, and the company was instructed to make many structural changes for a safer future experience. Due to this reason, all the Concorde flights were put on hold across the globe for a year.
Finally, on October 25th 2003, British Airways was forced to shut their last Concorde flight despite all the advised changes being made to the aeroplane. And this way, the generation of Concorde’s supersonic planes ended.




